
Did you know that nearly 92% of the world’s population lives in areas where air quality levels exceed the limits set by the World Health Organization (WHO)? This alarming statistic highlights the global scale of air pollution and its potential impact on our health.
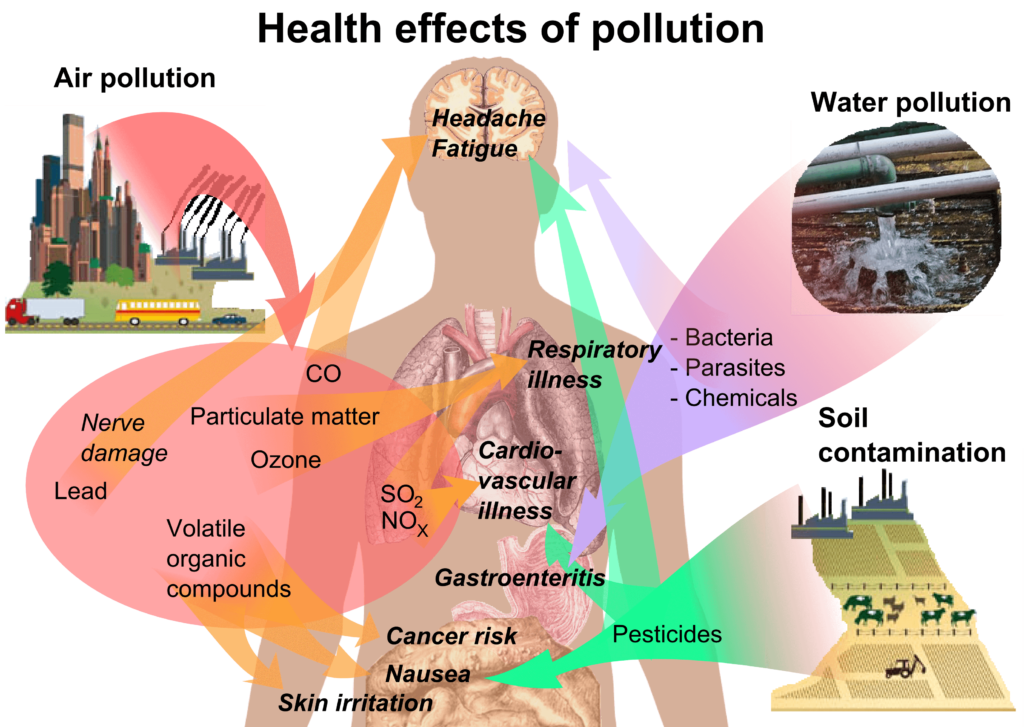
Pollution, particularly in urban areas, has become a silent yet dangerous threat to our well-being. Fine particulate matter (PM2.5), vehicle emissions, and industrial pollutants are all contributors to air quality degradation. These pollutants can have severe health consequences, including respiratory issues, exacerbation of allergies, and the development of long-term diseases such as asthma, bronchitis, and even heart disease.
As pollution levels continue to rise, it is essential to recognize the importance of protecting ourselves from its harmful effects—especially through effective protection methods like face masks.
The Growing Pollution Crisis

Air pollution is an escalating problem that affects cities worldwide, and the situation is only getting worse. According to the Global Burden of Disease Study, air pollution is responsible for over 7 million deaths annually, making it one of the leading environmental health risks. Urban areas, in particular, are facing severe pollution levels due to rapid industrialization, growing populations, and increased vehicular traffic.
One of the primary sources of urban pollution is vehicle emissions. As more people flock to cities, the number of cars, buses, and trucks on the roads has skyrocketed, leading to higher levels of nitrogen dioxide, carbon monoxide, and particulate matter. These harmful pollutants contribute significantly to poor air quality, especially during peak traffic hours when air pollution is at its highest.
In addition to vehicles, industrial activities also play a massive role in worsening air quality. Factories, power plants, and other industries release a variety of toxic substances into the air, including sulfur dioxide, volatile organic compounds, and heavy metals, further polluting the environment.
Another contributor to air pollution that is often overlooked is construction dust. In rapidly growing cities, construction sites are a constant source of airborne particulate matter, which can negatively impact health, especially for vulnerable populations.
But pollution isn’t limited to just outdoor air quality. In fact, indoor air pollution can be just as harmful. With the rise of energy-efficient buildings and homes, which are sealed tightly to conserve energy, indoor pollutants—such as tobacco smoke, household cleaning products, and even allergens—can build up to dangerous levels. The absence of proper ventilation in these enclosed spaces means that harmful particles and gases can linger inside, further contributing to health risks.
How Pollution Affects Our Health
Air pollution doesn’t just make the air look hazy—it has serious, long-term effects on our health, particularly on the respiratory system. Prolonged exposure to pollutants can lead to the development of various lung diseases, including asthma, chronic bronchitis, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). For people already living with these conditions, air pollution can worsen symptoms and increase the frequency of flare-ups, making it harder to breathe and carry out daily activities.
Fine particulate matter (PM2.5), which is a major component of air pollution, is especially harmful. These tiny particles, measuring just 2.5 microns or smaller, are so small that they can easily pass through the nose and throat, entering deep into the lungs and bloodstream. Once in the body, PM2.5 particles can cause inflammation, lung damage, and even increase the risk of heart disease and stroke. Studies have shown that long-term exposure to PM2.5 can also increase the risk of lung cancer.
For example, in cities with high levels of air pollution, such as New Delhi, Beijing, and Mexico City, there has been a significant increase in hospital admissions related to respiratory issues. The Air Quality Index (AQI), a tool used to measure air pollution levels, often reports hazardous levels in these regions, contributing to a rise in health problems. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), about 4.2 million deaths each year are linked to outdoor air pollution, with a large portion resulting from diseases related to lung and heart conditions caused by pollutants like PM2.5.
The impact of pollution on health isn’t limited to those already suffering from respiratory illnesses. Even healthy individuals can experience short-term effects such as coughing, shortness of breath, eye irritation, and fatigue. Children, the elderly, and people with pre-existing health conditions are particularly vulnerable to the dangers of air pollution.
How Face Masks Provide Protection
Face masks are one of the most effective and accessible ways to protect ourselves from harmful pollutants in the air. These masks work by acting as a physical barrier that filters out harmful particles and gases, preventing them from entering the respiratory system. By wearing a high-quality face mask, we can block a significant portion of harmful pollutants, such as PM2.5, vehicle exhaust, and industrial emissions, which are often too small to be filtered by our body’s natural defenses.
Different face masks offer varying levels of protection, and understanding these differences is crucial when selecting the right one. Below are some of the most commonly used face masks for pollution protection:
N95 Masks: These masks are among the most popular for pollution protection, especially in cities with high air pollution levels. They filter out 95% of airborne particles, including dust, pollen, and PM2.5. The N95 mask is designed to create a tight seal around the nose and mouth, preventing polluted air from bypassing the mask. This level of filtration makes N95 masks a go-to option for both everyday use and protection in hazardous conditions.
N99 Masks: Offering 99% filtration efficiency, N99 masks provide an even higher level of protection compared to N95 masks. These masks are ideal for areas with extreme levels of pollution, providing greater defense against both large and fine particles. They are commonly used in environments where pollution levels are hazardous, such as during smog events or near heavy traffic.
P100 Masks: The highest filtration standard, P100 masks block 99.97% of airborne particles, including harmful pollutants and viruses. While they are more commonly used in industrial settings, P100 masks offer the best protection for individuals who are particularly sensitive to pollutants or work in environments with significant airborne hazards.
It’s essential to note that not all face masks are created equal. While pollution face masks are specifically designed to filter out harmful particles, regular masks like cloth masks and surgical masks are not as effective in protecting against air pollution.
Cloth Masks: These masks, while useful for protecting against large droplets and some bacteria, do not provide sufficient protection against fine particulate matter like PM2.5. Cloth masks may have multiple layers, but they do not offer the same level of filtration as N95 or N99 masks. However, they can still be beneficial in everyday situations when air quality is relatively good.
Surgical Masks: Surgical masks are designed primarily for medical use to protect against viruses and bacteria rather than air pollutants. They provide limited protection against particulate matter and are not as effective as pollution-specific masks for blocking fine particles or gases.
Key Benefits of Wearing Pollution Face Masks
Wearing a pollution face mask offers numerous health benefits, especially for individuals living in areas with high levels of air pollution. Below are some of the key advantages of wearing a pollution-specific mask:
Protection from Particulate Matter (PM2.5, Dust, Pollen)
Pollution face masks are designed to filter out harmful particulate matter, especially PM2.5, which is one of the most dangerous pollutants. PM2.5 particles are tiny, measuring just 2.5 microns or smaller, and can easily penetrate the respiratory system, reaching deep into the lungs and bloodstream. Wearing a face mask with high filtration efficiency, such as an N95 or N99 mask, can block up to 95-99% of these harmful particles, helping to reduce the risk of respiratory issues like asthma, bronchitis, and even long-term lung damage.
A great example of a highly efficient pollution face mask is the SWASA Anti Pollution Face Mask. With an N95 filtration rating, this mask provides over 95% filtration efficiency, offering excellent protection against harmful pollutants like PM2.5, dust, and pollen. Its advanced nanofiber technology ensures that harmful particles are blocked while still allowing for easy breathing. This makes it an ideal choice for individuals in high-pollution environments.
Reducing the Risk of Respiratory Conditions
Prolonged exposure to air pollution is a known contributor to various respiratory conditions, including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, and bronchitis. By wearing a high-quality face mask, you can significantly lower your risk of developing these conditions or experiencing worsening symptoms if you’re already affected. Pollution face masks provide a shield against toxic particles and gases that irritate the lungs and trigger allergic reactions. For those living in areas with consistent air quality issues, wearing a mask can be a life-saving habit, reducing the chances of long-term health problems.
Blocking Harmful Gases and Chemicals (Carbon Monoxide, Nitrogen Dioxide, etc.)
In addition to fine particulate matter, pollution face masks also help filter out harmful gases and chemicals commonly found in polluted air, such as carbon monoxide (CO), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), and sulfur dioxide (SO2). These gases are known to contribute to serious health problems, including heart disease, stroke, and cancer. The SWASA Anti Pollution Face Mask is particularly effective in this regard, providing protection against not just particles, but also harmful gases in polluted environments.
Enhancing Overall Well-Being, Especially in High-Pollution Areas
Beyond protecting against specific health conditions, pollution face masks help improve overall well-being, particularly for individuals living in high-pollution areas. Wearing a face mask can help you breathe easier, reduce fatigue, and prevent headaches, which are common symptoms of poor air quality. People who are frequently exposed to pollution, such as commuters, outdoor workers, or residents of cities with high smog levels, often report feeling less stressed and healthier when wearing a mask regularly. The SWASA Anti Pollution Face Mask, with its comfortable fit, reusable design, and high protection, enhances overall well-being and is a great choice for daily protection against the effects of pollution.
When and Where to Wear Pollution Face Masks
Wearing a pollution face mask can make a significant difference in protecting your health in environments where the air quality is compromised. Here are some key situations and locations where wearing a pollution face mask is essential:
During Morning and Evening Traffic Hours
One of the times when air pollution is at its peak is during rush hour, when thousands of vehicles flood the streets, emitting harmful pollutants like carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides. The morning and evening traffic hours are often the worst in terms of air quality, especially in congested urban areas. If you commute by bike, walk, or use public transportation, wearing a pollution face mask can help you protect yourself from inhaling harmful particles and gases while you’re exposed to high traffic pollution levels.
In Crowded Public Places
In densely populated areas—whether it’s a crowded marketplace, busy subway station, or public event—pollution levels can rise due to the increased presence of vehicles, construction, and other urban activities. These places often have elevated levels of dust, vehicle emissions, and industrial pollutants in the air. A face mask can be especially beneficial in such crowded environments, where you’re likely to breathe in higher concentrations of pollutants.
In High-Pollution Cities
Cities with poor air quality, such as New Delhi, Beijing, Mexico City, and Jakarta, often experience year-round pollution, with particulate matter regularly exceeding safe levels. For residents and visitors in these cities, wearing a pollution face mask is a practical step to reduce exposure to harmful particles like PM2.5. In high-pollution areas, a face mask becomes an essential accessory, helping safeguard your respiratory health from the constant presence of air contaminants.
Seasonal Pollution (Winter Smog, Summer Ozone Levels)
Pollution levels are not constant throughout the year—certain seasons can exacerbate air quality issues, especially in cities where weather patterns play a role in trapping pollutants close to the ground.
Winter Smog: During colder months, air pollution levels tend to spike, particularly in cities where temperature inversions trap pollutants in the air. In many regions, winter smog is common, which is a combination of fossil fuel combustion, home heating, and vehicle emissions. This results in thick, low-lying clouds of pollutants, which can be especially harmful to people with respiratory issues.
Summer Ozone Levels: In the summer, increased sunlight and heat can lead to the formation of ground-level ozone, which is a dangerous pollutant. Ozone is formed when sunlight reacts with pollutants like volatile organic compounds (VOCs) from vehicles and industrial emissions. This ozone can irritate the lungs, causing coughing, shortness of breath, and worsening asthma symptoms. Wearing a pollution face mask during hot, sunny days can help protect you from inhaling these harmful ozone levels.
Final Thoughts
As air pollution continues to pose a significant threat to public health, wearing a pollution face mask is no longer just a precaution—it’s a necessity. The long-term benefits of protecting yourself from harmful pollutants cannot be overstated. Whether you’re commuting through congested streets, spending time in crowded public spaces, or living in a high-pollution city, a quality face mask can reduce your exposure to dangerous particles and gases that can damage your lungs, heart, and overall well-being.
When choosing a pollution face mask, it’s important to prioritize both high protection and comfort. Masks with high filtration capabilities, such as N95 or N99, provide the best defense against harmful pollutants. However, comfort is just as important, especially if you plan to wear the mask daily. Make sure to choose a mask that fits well and is breathable, so you can wear it comfortably for long periods without feeling restricted.
We encourage you to explore the various face mask options available to find the one that best suits your needs. Whether you’re looking for maximum protection against fine particulate matter or a mask for daily use in a moderately polluted area, there’s a mask out there that’s right for you. Protecting your health is the most important investment you can make, and it starts with choosing the right mask to safeguard you from the harmful effects of air pollution.

